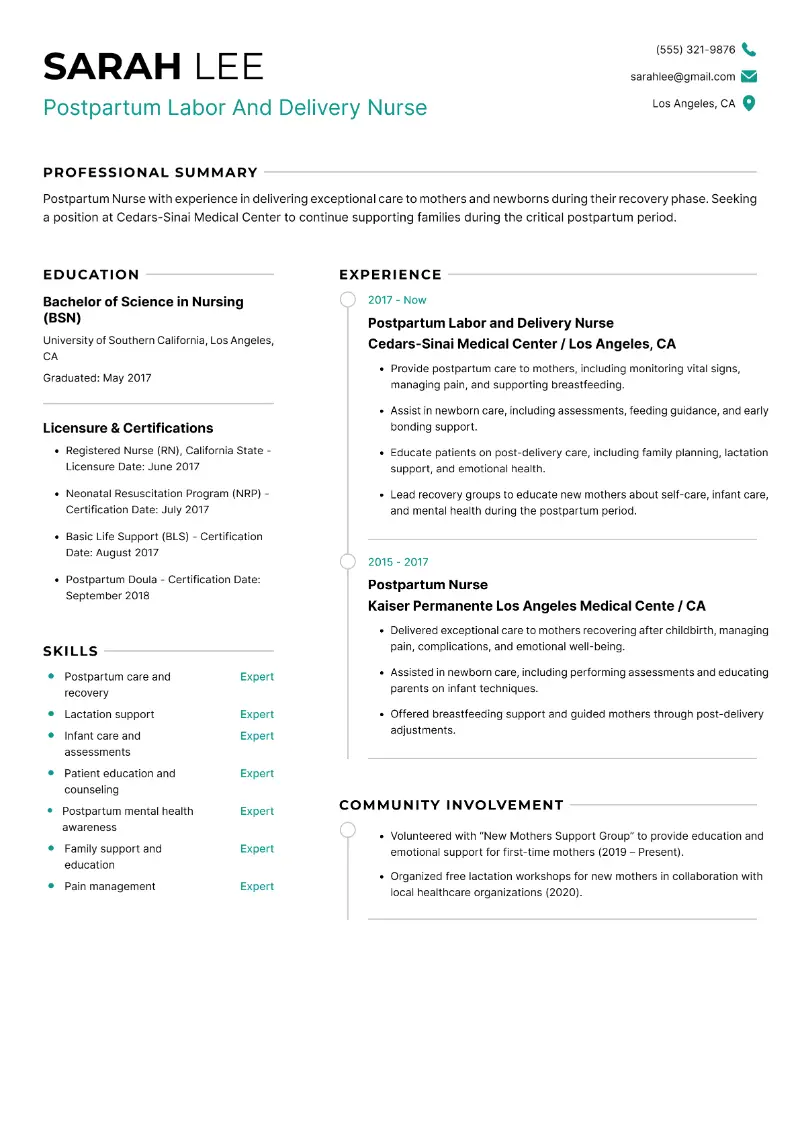
Nursing skills for a resume are crucial in demonstrating your ability to provide exceptional care and excel in a fast-paced healthcare environment.
Whether you're an experienced caregiver or just starting your career, it's important to highlight a blend of clinical expertise, soft skills, and professional accomplishments that align with the specific demands of the role.
In this article, we will outline key skills for nursing to feature on your application and offer tips on how to present them effectively to increase your chances of landing your desired job.
What are nursing skills?
Nursing resume skills refer to the various abilities, knowledge, and competencies that professionals must possess to give safe, effective, and compassionate patient care.
These can be broadly categorized into clinical, technical, and interpersonal capacities, and they are essential for a nurse to perform their job duties effectively.
Skills to put on nursing resume
Nursing is a multifaceted profession that demands proficiency across various areas of expertise.
In healthcare, skills are the foundation upon which effective patient care is built. They ensure safety, improve efficiency, and contribute to better outcomes while enhancing professional satisfaction and growth.
Clinical nursing skills list
- 1. Patient Assessment
- Physical Examination. Performing thorough assessments through inspection, palpation, and auscultation to check for abnormalities.
- History Review. Collecting detailed background information regarding medical, family, and lifestyle factors.
- Vital Signs Monitoring. Accurately measuring blood pressure, heart, respiration rate, body temperature, and pain intensity.
- Pain Evaluation. Using tools like the numeric pain scale to assess and manage discomfort.
- Neurological Evaluation. Monitoring mental status, reflexes, coordination, and consciousness.
- 2. Patient Care
- Wound Management. Cleaning, dressing, and observing wounds to ensure healing and prevent infection.
- Personal Hygiene Assistance. Helping with bathing, grooming, and maintaining cleanliness for patients with limited mobility.
- Infection Control Practices. Ensuring sterile techniques, performing hand hygiene, and managing isolation precautions.
- Temperature Regulation. Adjusting environment and applying methods to stabilize body temperature.
- 3. Medication Administration
- Oral. Administering prescribed pills, liquids, or tablets while ensuring correct dosage and timing.
- Intravenous (IV). Managing IV lines for fluid and drug delivery, checking compatibility and flow rates.
- Injection Techniques. Safely giving intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intravenous injections.
- Documentation. Accurately recording medications given, noting reactions, and effects.
- Dosage Calculation. Calculating medication quantities based on weight, age, or specific patient factors.
- 4. Clinical Interventions
- Blood Transfusion. Preparing and delivering blood products while monitoring for adverse reactions.
- Oxygen Therapy. Executing supplemental oxygen through different delivery methods and observing patient response.
- ECG/EKG Interpretation. Conducting electrocardiogram tests to diagnosing abnormalities.
- Chest Tube Management. Inserting and caring for chest tubes to help with lung re-expansion or drainage.
- 5. Critical Care Skills
- Basic Life Support (BLS). Performing CPR and using defibrillators during emergencies to save lives.
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Handling techniques for cardiac arrest and critical cardiovascular events.
- Cardiac Rhythm: Identifying irregular heart rhythms and intervening to stabilize patients.
- Sepsis Identification. Recognizing signs of sepsis and implementing treatment protocols quickly.
- 6. Nutrition and Hydration
- Nutritional Assessment. Evaluating dietary needs and recommending appropriate sustenance based on patient condition.
- Enteral Feeding. Allocating dietary intake through feeding tubes for patients unable to eat normally.
- Parenteral Provisions. Delivering nutrients intravenously when oral or enteral methods are not possible.
- Hydration. Managing fluid balance and adjusting interventions to maintain proper hydration levels.
- 7. Postoperative Care
- Recovery Monitoring. Observing patients after surgery, checking vital signs, and controlling pain.
- Complication Prevention. Recognizing early signs of issues such as infections, bleeding, or thromboembolic events.
- Pain Control. Administering medications and therapies to manage discomfort after surgical procedures.
- Wound and Drain Care. Arranging surgical wounds, cleaning, and maintaining drains to prevent infections.
- 8. Palliative Care
- Symptom Management. Addressing pain and other symptoms with appropriate drug and non-pharmacological methods.
- Patient and Family Support. Assisting families and patients with decisions, end-of-life planning, and emotional care.
- Comfort Measures. Providing physical comfort through positioning, relaxation techniques, and dose.
- Grief Counseling. Offering emotional support to families experiencing loss and guiding them through the grieving process.
- 9. Patient Education
- Chronic Illness Management. Teaching patients how to handle chronic diseases, including lifestyle changes.
- Medication Education. Explaining correct pharmaceutical usage, potential side effects, and administration methods.
- Discharge Instructions. Preparing families for post-hospital care, follow-up visits, and rehabilitation.
- Health Promotion. Providing guidance on preventing illness through habits, vaccinations, and screenings.
- 10. Reporting
- Patient Record Keeping. Writing clear, concise, and accurate entries in medical records to document care, assessments, and responses.
- Care Plan Development. Creating, implementing, and adjusting care plans based on ongoing evaluations.
- Condition Monitoring. Documenting and communicating changes in a patient’s condition to the team.
- Legal and Ethical Documentation. Ensuring compliance with laws, patient privacy, and ethical standards.
Create your professional Resume in 10 minutes for FREE
Build My Resume
Hard skills for nursing
Hard skills are teachable knowledge sets that are usually acquired through formal education, training programs, or hands-on experience. They are measurable and often tested or assessed.
Examples of nursing skills for resume:
- 1. Medical Equipment Management
- IV Pump Operation. Configuring and overseeing pumps for fluid and medication infusion, ensuring accurate delivery.
- Ventilator Operation. Adjusting settings and monitoring ventilators for patients requiring respiratory support.
- ECG/EKG Setup. Positioning electrodes and interpreting heart activity to identify irregularities.
- Pulse Oximeter Use. Measuring blood oxygen levels to evaluate respiratory function.
- 2. Medication Administration
- Oral Dosing. Administering tablets, liquids, or capsules and ensuring accurate dosage and patient compliance.
- Infusion Devices. Programming infusion pumps for controlled medication delivery, such as in pain management.
- Injection Techniques. Delivering medications via intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intravenous methods, observing for reactions.
- Insulin Management. Implementing insulin to patients with diabetes, adjusting doses based on glucose levels.
- 3. Wound Care and Dressing
- Sterile Technique. Using infection-control methods when cleaning and dressing wounds to promote healing.
- Negative Pressure Wound Therapy. Applying vacuum-assisted systems to enhance healing in difficult wounds.
- Suture/Staple Removal. Carefully removing surgical stitches or staples, ensuring wound integrity.
- 4. Catheterization
- Urinary Catheter Insertion. Inserting and maintaining catheters to manage urine output for patients with urinary retention.
- Suprapubic Catheter Insertion. Performing catheter placements directly through the abdomen when traditional methods are not suitable.
- Catheter Care. Regularly cleaning and monitoring urinary catheters to prevent infections or blockages.
- 5. Diagnostic Testing
- Sample Collection. Accurately gathering urine, stool, or blood specimens for laboratory analysis.
- Blood Pressure Measurement. Monitoring and recording blood pressure, interpreting results for potential health issues.
- Peak Flow Monitoring. Exploiting devices to assess lung function, especially in patients with respiratory conditions.
- Telemetry Setup. Installing devices to monitor heart activity continuously and alerting teams to any abnormalities.
- 6. Respiratory Care
- Oxygen Therapy. Regulating oxygen through various delivery systems (e.g., nasal cannula, mask) and adjusting flow rates.
- Nebulizer Treatments. Delivering medication via nebulizers to treat conditions like asthma or COPD.
- Airway Suctioning. Performing suctioning to clear patients’ airways, especially in critical care or post-surgery.
- CPAP/BiPAP Management. Operating devices that help patients with sleep apnea or respiratory distress by assisting with airflow.
- 7. Telemetry and Monitoring
- Cardiac Rhythm Monitoring. Adopting telemetry devices to continuously observe and document heart rhythms.
- Capnography. Measuring exhaled carbon dioxide to assess the effectiveness of ventilation in sedated or critically ill patients.
- Temperature Monitoring. Using various methods to track and manage patient temperature, ensuring comfort and health.
- 8. Mobility and Rehabilitation Support
- Patient Transfer. Helping patients move from one position to another, such as from bed to chair, ensuring safety.
- Walking Assistance. Aiding patients in regaining mobility post-injury or surgery.
- Pressure Ulcer Prevention. Deploying repositioning techniques to prevent the formation of pressure sores in immobile patients.
- 9. Sedation and Anesthesia Assistance
- Sedation Administration. Administering sedative medications for minor procedures and monitoring the response.
- Anesthesia Equipment Setup. Assisting with anesthesia machines and ensuring the airways remain secure during surgery.
- Post-Sedation Recovery. Observing patients as they recover from anesthesia, ensuring a smooth transition back to consciousness.
- 10. Infection Prevention
- Disinfection Practices. Cleaning surfaces and medical tools thoroughly to prevent the spread of pathogens.
- Isolation Protocols. Following guidelines for isolating patients with contagious diseases to reduce cross-contamination.
- Sterilization. Ensuring instruments are sterilized before use in procedures to maintain safety and minimize infection risk.
Soft skills for nursing
Soft skills are interpersonal, communication, and emotional intelligence abilities that determine how well you interact with others and manage yourself in various situations. These are less tangible and are often learned through personal experience and social interactions.
Nursing skills to put on resume:
- Communication: The ability to effectively convey information to patients, families, and healthcare teams through both verbal and non-verbal methods.
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others to provide emotional support and comfort.
- Teamwork: Collaborating with healthcare colleagues to ensure coordinated and efficient patient care.
- Adaptability: Adjusting to new challenges, patient needs, and work environments with flexibility and openness.
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks efficiently to meet deadlines and provide optimal care in a timely manner.
- Problem-solving: Identifying issues and creating actionable solutions to improve patient care and outcomes.
- Emotional Resilience: Maintaining composure and strength in emotionally charged or difficult situations.
- Active Listening: Fully focusing on what others are saying and responding thoughtfully to affirm clear understanding.
- Conflict Resolution: Mediating disagreements or tensions among patients, families, or coworkers in a respectful manner.
- Leadership: Guiding and motivating others, providing direction in patient care while fostering a supportive environment.
- Cultural Competence: Recognizing and respecting cultural differences, delivering care that is inclusive and sensitive to diverse backgrounds.
- Attention to Detail: Focusing on the precise details of tasks such as medication administration or patient assessment to prevent errors.
- Professionalism: Exhibiting ethical behavior, responsibility, and respect in all interactions with patients, families, and peers.
- Stress Management: Maintaining mental clarity and focus under pressure, managing stress to validate continued high-quality care.
Nursing skills resume examples
Sample of nurse skills for resume
Shelia K. Ramirez
Wild Rose, WI 54984
Phone: (555) 123-4567 | Email: sheliakramirez@email.comObjective
Compassionate and dedicated Registered Nurse with experience in clinical and healthcare settings. Proficient in administering treatments, patient care, and medical procedures while maintaining the highest level of care standards.
Licenses
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS) – Certified until 2026 (Issued: January 2023)
- Basic Life Support (BLS) – American Heart Association, Certified until 2026 (Issued: January 2023)
- Registered Nurse (RN) – Wisconsin Board of Nursing, License #2345678 (Issued: June 2015)
Professional Experience
Registered Nurse
St. Mary's Hospital – Wild Rose, WI
January 2020 – Present
- Administer and monitor medications, treatments, and therapies to patients in compliance with their care plans and physician orders.
- Actively collaborate with multidisciplinary healthcare teams to ensure seamless patient care and treatment protocols.
- Provide emotional support to patients and their families, helping them navigate complex health issues and providing compassionate care in critical situations.
- Lead patient education initiatives, focusing on post-operative care, chronic illness management, and preventative health measures.
Nurse Manager
Oakwood Care Center – Wild Rose, WI
June 2017 – December 2019
- Developed and implemented care plans, prioritizing patients’ physical, emotional, and psychological needs in long-term care settings.
- Led staff training programs and in-service education, ensuring continuous professional development and adherence to best practices.
- Implemented quality improvement initiatives to enhance patient satisfaction, reduce incidents, and improve overall service delivery.
Registered Nurse – Pediatric Unit
Sunnydale Children's Hospital – Green Bay, WI
June 2015 – May 2017
- Delivered compassionate care to patients, assessing and monitoring their health while providing age-appropriate medical interventions.
- Administered vaccinations, IV fluids, and medications, adjusting dosages based on age and weight.
- Ensured a safe and comforting environment for children, reducing anxiety through age-appropriate explanations and care approaches.
Education
Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN)
University of Wisconsin – Green Bay, WI
Graduated: May 2015
Skills
- Administration of medications (oral, IV, injections, subcutaneous)
- Post-operative care and monitoring
- ECG/EKG interpretation and management
- Oxygen therapy, intubation, and ventilation support
- Blood glucose monitoring and insulin administration
- Compassionate patient care
- Strong problem-solving and critical thinking abilities
Awards
- Nurse of the Year – St. Mary’s Hospital, 2023
- Employee of the Month – Oakwood Care Center, September 2018
- Excellence in Patient Care Award – Sunnydale Children’s Hospital, 2016
References
Available upon request.
Examples of RN resume with skills
Conclusion
In conclusion, showcasing the right skills for nursing resume is essential for standing out in a competitive healthcare job market.
A well-crafted application that reflects a balance of hands-on experience and strong interpersonal abilities can significantly increase a nurse’s chances of securing their desired position.
Create your professional Resume in 10 minutes for FREE
Build My Resume