Deciding what to choose - a portfolio vs a resume - is crucial for effectively showcasing your qualifications. Both documents serve distinct purposes in presenting your professional abilities, but they cater to different needs.
This article will explore what each document entails, highlight the key difference between a portfolio and a resume, and offer practical writing tips for creating both types of the job application materials.
What is a resume?
A resume is a concise document that summarizes an individual's work experience, education, skills, and accomplishments. This is the primary tool used to apply for a job and to secure an interview.
Usually, stick to one page resume format, however, very experienced professionals may choose to go over this limit.
Role of a resume:
- Introduction to employers. Provides a snapshot of your professional background.
- Highlight relevant experience. Emphasizes job-specific skills and qualifications.
- Demonstrate achievements. Showcases outcomes of work and career milestones.
- Initial screening tool. Helps HR quickly identify suitable candidates for the position.
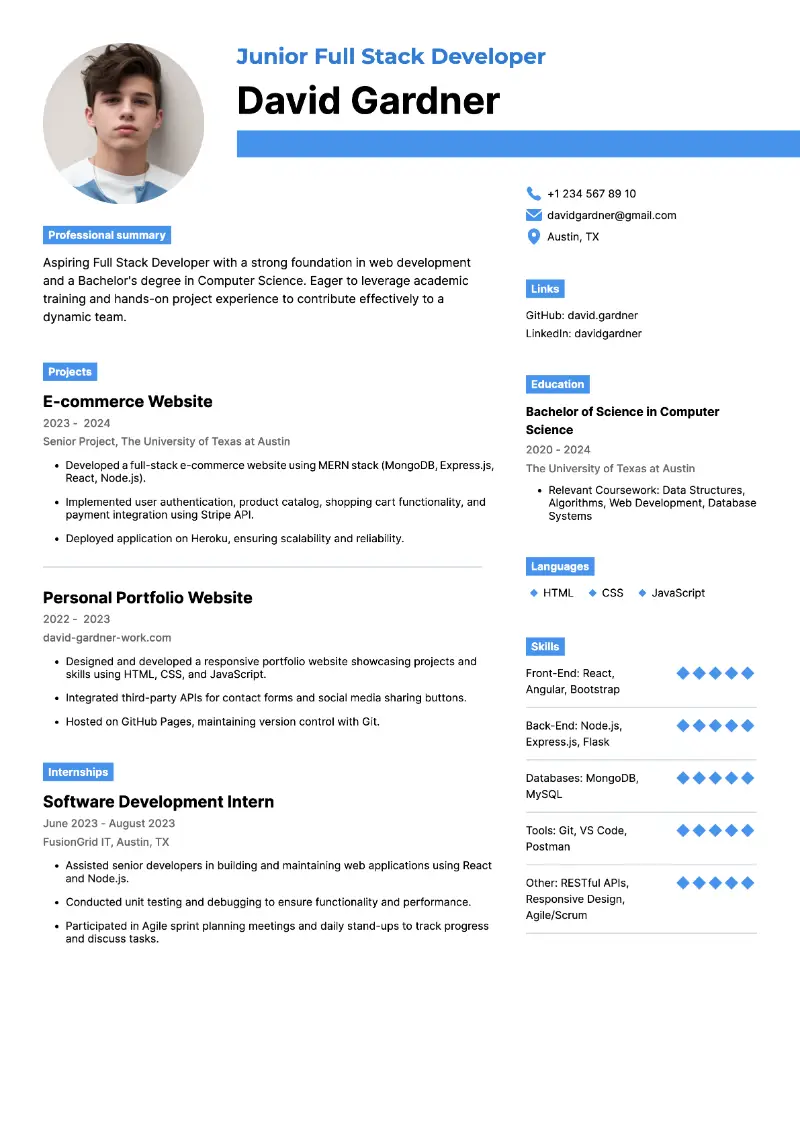
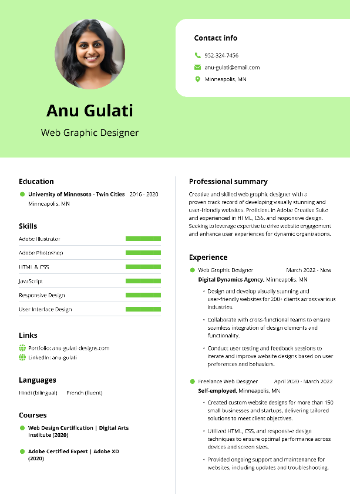
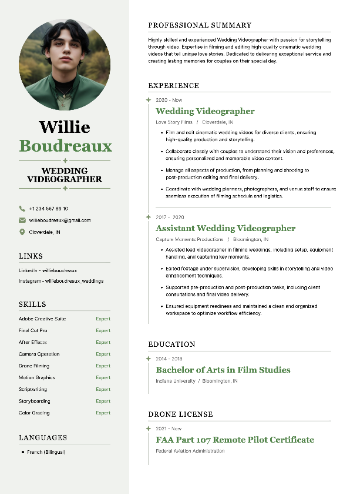
Resume examples:
What is a portfolio?
A portfolio is a comprehensive collection of work samples, projects, and other evidence of skills and experiences.
Unlike a resume, which is text-based, a portfolio is often more visual and detailed, showcasing actual work products and creative outputs. Portfolios are commonly used in fields like design, writing, and photography but are becoming increasingly relevant in other industries.
Role of a portfolio:
- Showcase work quality. Provides concrete examples of your work and abilities.
- Detail project contributions. Highlights your role and impact on specific projects.
- Illustrate skills in action. Demonstrates how you apply your professional skills in real-world scenarios.
- Build credibility. Enhances your professional credibility through tangible proof of your expertise.
Portfolio website examples:
Here are five examples of websites where you can create a portfolio, each catering to different professions and needs.
| Website | Description | Ideal for |
|---|---|---|
| Behance | A service owned by Adobe that allows creatives to display their projects and connect with others in the industry. | Artists and other creatives |
| Helps build portfolios and personal brands by sharing professional photos, behind-the-scenes shots, and personal content. | Photographers, models, fashion influencers | |
| GitHub | A platform for developers to host and review code, manage projects, and collaborate on software development. | Data scientists, programmers, DevOps engineers |
| Tableau Public | Allows to create and share interactive data visualizations and dashboards with a wide audience. | Data analysts, business analysts, researchers |
| Dribbble | A community for indicating creative work, finding inspiration, and connecting with potential clients and employers. | Designers, illustrators, UI/UX designers |
| A professional networking site that enables users to create detailed portfolios showcasing projects and recommendations. | Applicants across all industries seeking to build a comprehensive online presence |
Resume vs portfolio: differences
Understanding the key difference between a resume and a portfolio is necessary for choosing the right format for your career highlights. Let's compare the two documents.
Purpose
- The primary purpose of a resume is to provide an overview of your qualifications, past experiences, and key skills. It's a tool for employers to quickly assess whether you meet the basic criteria for the position.
- A portfolio goes beyond the simple listing of past jobs by showcasing actual work. It provides evidence of your abilities and achievements through detailed examples, helping potential employers or clients understand the scope of your abilities.
Length
- Typically, resumes are concise, spanning one to two pages. This brevity is crucial for capturing the attention of hiring managers who often review many applications.
- There is no fixed length for portfolios as it can vary significantly based on the amount and nature of the content. They often include multiple sections and detailed descriptions of work, which takes up much more space than a resume.
Content
- Resumes are predominantly text-based, focusing on job titles, dates of employment, responsibilities, education, and skills.
- Portfolios combine text and visuals. They include work samples, case studies, process descriptions, and visual elements such as images, videos, or code snippets.
Focus
- A resume emphasizes your professional history, aligning your background with the specific requirements of the job you are applying for.
- A portfolio focuses on the quality and impact of your work, providing detailed insights into specific projects.
Use
- Resumes are used across all industries and are a fundamental part of any job application process. They are submitted along with cover letters and other application materials.
- Portfolios are particularly common in creative, technical, and project-based fields. While not universally required, they are highly valuable in industries where demonstrating work samples is needed.
Update Frequency
- You should update your resume periodically, typically when you change jobs, gain new skills, or achieve significant accomplishments.
- A portfolio requires more frequent updates as you complete new projects or produce new work.
Presentation
- Resumes follow a structured, formal format. They adhere to conventional layouts and styles to ensure clarity and readability.
- Portfolios offer greater flexibility in presentation. They can be designed creatively to reflect your personal brand and style. Digital portfolios, in particular, allow for interactive and multimedia elements.
Summary table
| Aspect | Portfolio | Resume |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Showcases work samples and projects in detail. | Summarizes professional experience and skills. |
| Content | Project examples, designs, case studies, visuals. | Job roles, abilities, achievements, and education. |
| Length | Typically longer and detailed. | Usually 1-2 pages, concise. |
| Format | Digital (website/PDF) or physical (binder). | Text document (PDF/Word). |
| Visuals | Highly visual, with images or charts. | Mostly text, minimal visuals. |
| Customization | Highlights specific projects for targeted roles. | Emphasizes relevant experience for each job. |
| Best For | Creative, project-based roles (designers, writers). | Standard for most industries and roles. |
How to write a resume?
Building a resume requires a strategic approach and close examination of the desired position. Generally, you have to follow a specific resume structure that includes key sections.
What to include on a resume:
- Contact information. Name, phone number, email address, LinkedIn profile.
- Professional summary or objective. Brief statement highlighting your career goals and key qualifications.
- Work experience. List of jobs, including job titles, company names, locations, and dates of employment.
- Education. Degrees, institutions, and graduation dates.
- Skills. Relevant skills that align with the job you are applying for.
- Certifications. Any applicable professional certifications or licenses.
- Achievements. Specific accomplishments and recognitions.
- Professional associations. Memberships in industry organizations.
- Portfolio. A link to your personal website with work samples.
- Volunteering. Unpaid work that displays community involvement.
How to include a portfolio in a resume?
There are several ways how you can integrate your portfolio into the resume.
Here are some common techniques:
- Add a URL to your online portfolio in the contact information section of your resume.
- Include links to relevant work samples alongside descriptions of your job roles.
- Share a link to your portfolio in the footer or header of your resume.
Create your professional Resume in 10 minutes for FREE
Build My Resume
How to make a portfolio?
Once you choose the platform (or get your own web domain), you can get creative and structure your portfolio in any way you want. However, some key information still needs to be included.
Suggested portfolio format:
- Introduction. A brief biography, including your professional background and areas of expertise.
- Work samples. Examples of your best work, such as designs, writing samples, project reports, or code snippets.
- Case studies. Detailed accounts of specific projects, including your role, challenges faced, and outcomes achieved.
- Skills and tools. A list of key abilities and software you are proficient in, often demonstrated through your work samples.
- Client testimonials. Positive feedback from clients or colleagues, if applicable.
- Awards. Any formal recognitions you have received.
- Contact information. Ways for potential employers or clients to reach you.
- Resume. An updated copy of your resume for reference.
- Blog or insights. Articles or posts where you share industry knowledge or reflections.
Resume with portfolio examples
Portfolio vs resume: FAQ
- Can I use a portfolio instead of a resume?
- No, a portfolio is not a substitute for a resume. They serve different purposes. A resume provides a summary of qualifications, while a portfolio offers detailed proof of work and skills.
- Should I include personal projects in my portfolio?
- Yes, including them can exhibit your passion, creativity, and initiative, especially if they are relevant to your career goals.
- How detailed should my work samples be in my portfolio?
- Provide enough information to demonstrate your skills and the impact of your work. Include context, challenges faced, your specific contributions, and the outcomes.
- Is it okay to include a portfolio link on a traditional resume?
- Yes, including a link to your portfolio on your resume is a great way to provide employers with additional information and examples of your work.
- Can a portfolio be a physical document, or should it be digital?
- Portfolios can be both physical and digital. However, digital portfolios are more accessible and easier to update and share.
- How can I make my portfolio stand out?
- Focus on high-quality work samples, clear organization, and a professional design. Tailor your portfolio to your target audience and ensure it effectively displays your unique skills and experiences.
- What are common mistakes to avoid in a resume?
- These include typos, irrelevant information, lack of focus, and failure to quantify achievements. Ensure your resume is concise, pertinent, and error-free.
- What are common mistakes to avoid in a portfolio?
- Refrain clutter, poor organization, and low-quality work samples. Ensure your portfolio is easy to navigate, visually appealing, and exposes your best work.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the debate of portfolio vs resume highlights the distinct roles each tool plays in the job search strategy. A resume provides a snapshot of your qualifications, while a portfolio delivers a comprehensive showcase of your work.
By properly structuring your resume and portfolio and keeping both up-to-date, you can present yourself as a compelling candidate to potential employers.